Introduction
Cryptocurrencies have seen large scale adoption in recent times. Terms like buy and hodl have become an investing mantra denoting a long term approach to cryptocurrency investing.
As more and more people hodl cryptos, there was a need to bring in real utility to the ecosystem rather than pure speculation. Every crypto is unique in terms of utility it offers its potential upside based on its inflation and many other factors. Understanding the supply and demand characteristics of cryptocurrency to determine the long term value of an asset is called tokenomics.
As the industry grew more and more innovative teams came up with innovative ways to incentivise users to hold their native tokens. Along with the advent of defi which for the first time facilitated peer to peer finance at a global scale in a decentralised, permissionless way, Dapp developers got the freedom to launch their token with unique tokenomics on these permissionless defi protocols.
All the above factors gave rise to yield farming. Here are some popular ways in which yield is generated on the protocols:
Lending: Instead of just holding the tokens, you can lend your tokens. Borrowers can come in and take a loan and pay the interest. The interest earned is paid back to all the lenders. The whole process is done transparently since smart contracts are built on a public blockchain. Currently, Solend is the most used lending protocol on Solana.
Liquidity provisioning: You can provide liquidity to various pools on decentralised exchanges. You provide a pair of tokens in a 50:50 ratio as liquidity in the pool. You earn trading fees for every swap for those two tokens. Uniswap, Curve are currently the biggest decentralised exchanges.
Staking: Staking helps secure the blockchain network achieving Sybil resistance. Staking rewards are given to all validators in a PoS network. You can delegate your tokens to them to earn a part of their staking rewards, typically the longer you stake, the higher the rewards you get. Staking rewards are typically funded by inflation for that token. Although staking does not come under defi, some liquid staking protocols can be used to convert your staked crypto into liquid crypto usable in various defi protocols. Lido is currently the most widely used liquid staking service.
Beyond the typical protocol fees you earn, these protocols also give out their native tokens to attract users. For example, Compound gives out Comp governance tokens on lending on their platform.
Currently, the biggest problem in all these yield farming strategies is sustainability. During the bootstrapping phase, Dapps incentivise users by promising ridiculously high APYs typically by giving away their native tokens. These are known as liquidity mining programmes. As you can guess these APYs are paid out by inflating the token supply which naturally leads to negative price action.
This is not sustainable as when the APY comes down. Users will shift to a newer dapp that promises higher APY.
There was a need for a sustainable source of passive yield without shifting from one Dapps to another to take advantage of all the liquidity mining programmes.
This gave rise to defi dapps offering Vault strategies, where once you deposit your cryptos, the tech helps maximize yield through shifting capital, auto-compounding, and rebalancing. Custody, and responsibility, for your holdings, remains yours. You can withdraw anytime. Yearn finance on fantom and Ethereum is currently the most widely used dapp for vault strategies.
Yearn may have solved the problem of shifting from one dapp to another for liquidity mining but still, the fundamental fact remains that none of these liquidity mining programmes is sustainable. Yields will eventually dry up.
There was a need for structured yield generating products along with the above mentions automated vault strategies to simplify the UX for largely fragmented and manual yield generation.
Here is where Katana comes in.
Katana Introduction
Katana is building the yield generation primitive for Solana.
At its core, Katana simplifies yield generation on Solana by identifying, composing, and packaging the best strategies in DeFi into accessible yield products.
What makes Katana different from current yield generating protocols?
Sustainable Yield
Katana generates yield by enabling users to express views on price action, composing such views into a suite of packaged yield products. In this way, Katana is not dependent on liquidity mining programs and thus offers a differentiated and more sustainable source of yield for any given risk-return profile.
Automated Yield Generation
Katana automates and packages complex strategies into vaults, enabling users to passively access sophisticated strategies by simply depositing their funds into their vault of choice.
Strategy Optimization
Katana optimizes everything from strike selection to order execution, ensuring its users earn the best yields for their chosen strategy.
Simplified User Experience
Katana vaults allow the users to interact with a simple interface, abstracting away the complexity of the underlying strategies and derivative protocols.
Built On Solana
Solana's performance and affordability offer Katana several key advantages, including:
Extremely low transaction fees
An improved user experience
Wider design space of strategies
Katana aims to become an evolving and permissionless protocol, allowing anyone to access, contribute to, and build upon the best yield products in the Solana ecosystem.
By embracing the ethos of Web3 and DeFi, Katana looks to transform yield generation for the better. In building a truly decentralized and permissionless protocol for yield generation, Katana's vision is to:
Democratize access to sophisticated and optimized yield strategies
Enable anyone to contribute strategies and products to the core protocol layer
Allow developers to permissionlessly build products and protocols on top of Katana that source yield from the base layer
Transfer ownership to the community
Better align incentives and distribute upside to all stakeholders of the protocol
Katana aims to provide two provide 2 main types of strategies to its users:
Structured Products
Covered calls and put selling strategies for popular assets
Sustainable yield is generated by expressing a market view
Abstracts away the complexity of the underlying derivative strategies
Fully automated for the user, automatically rolling over positions at the end of each period
Automated Vault Strategies
Passive method to earn yield on a chosen base asset
Span a wider array of yield farming opportunities
Strategies will be changed as new opportunities arise, enabling depositors to consistently earn the best yields available
Fully automated execution for the user
Currently, structured products — consisting of covered calls and put selling strategies - are live on the main net.
In the next section, we will discuss these strategies more in-depth, but first, we must understand jargon like call and put options in the world of finance.
Futures contract, Call and Put Options
So what is a futures contract?
Currently 1 SOL = $1
You think it will be worth $7 in 7 days.
Your friend who has 1 SOL comes up to you and promises to sell you his SOL for $1 after 7 days, no matter what the actual price is on that day. You agree to pay after 7 days.
Congrats, you just entered a futures contract.
Scenario 1: If Sol price increases to $7 after 7 days as you predicted, you can buy 1 SOL from your friend for $1 as per your agreement and you can then sell it for $7 in the open market, making a profit of $6.
Scenario 2: If Sol price drops to $0.25 after 7 days, you still have to buy 1 SOL from your friend for $1. You just made a loss of $0.75.
In reality, you don’t really have to exchange the asset, if scenario 1 plays out, your friend will just pay you $6 and if scenario 2 plays out, you just pay your friend $0.75 to settle the contract.
This is how most of the exchanges work, you just settle in cash, instead of actually exchanging the asset.
That’s why futures are called ‘derivatives’ because the market derives value from an underlying asset without actually exchanging the asset.
Same as the futures contract, an options contract gives the buyer the right to buy the asset at a fixed price at a future date. However, there is no obligation on the part of the buyer to go through with the purchase. Nevertheless, should the buyer choose to buy the asset, the seller is obliged to sell it.
This is the only main difference between futures and options contracts, in a futures contract the buyer has the obligation to buy the asset at a future date whereas in the case of an options contract the buyer has no obligation to buy.
An option is a contract giving the buyer the right—but not the obligation—to buy (in the case of a call) or sell (in the case of a put) the underlying asset at a specific price on or before a certain date.
Call options allow you to buy tokens at a specific time.
Put options allow the selling of tokens at a specific time.
Call Options example:
Sol Price: $100
Will is very bullish on SOL and thinks that its price is going to rise past $100. He can do two things, he can just buy SOL currently at $100 and hodl or he can buy call options. Let us compare both the scenario, first let us see how he can buy a call option.
He pays $5 to buy the SOL May 30th $110 call option, he is buying the right to pay $110 (the strike price) for one SOL token on or before May 30th. The $5 he pays is called the premium. Let’s compare the outcomes of buying one of these calls for $5 to buying SOL for $100. Let’s look at the scenarios that could occur on May 30th:
Scenario 1 (The price of SOL rises):
Assuming that SOL has risen to $150. If Will had spot bought one SOL for $100, he would make $50 on his investment (+50%). However, If he had bought the May 30th $110 call for $5, he can purchase the coin for $110 and sell it for $150, netting $35 profit ($150 - $110 - $5). This is a 700% profit return on his $5!!!!. Will makes a greater return than had he simply spot bought SOL.
Scenario 2 (The price of SOL stays the same):
Assuming that SOL stays at $100. If Will had bought one SOL for $100, he would neither have made nor lost money. whereas, if he had bought the call for $5, he would lose $5. In this scenario, the option is worthless as the strike price is greater than the token price. In the case of the asset price not moving options can do poorly, Will lost his entire investment compared to being even had he spot bought the token.
Scenario 3 (The price of SOL falls):
Assuming that SOL falls to $50. If Will had spot bought one SOL for $100, he would lose $50 (-50%). If he had bought the call for $5, he would only lose $5. Will only lost $5 compared to losing $50 had he spot bought the token. Note that he still retained the upside potential in the case that SOL had increased in value.

Selling Call options:
Sol Price: $100
SOL has had a strong recent uptrend, however, Will thinks that there is no way the price of SOL will go above $150 (the strike price). He wants a way of profiting. Will might sell call options to accomplish this.
Will agrees to sell 1 call at $5, this allows him to collect the premium; Will will be paid $5 ($5 * 1). Let’s look at the scenarios that could occur:
Scenario 1 (The price of SOL rises):
If the price of SOL keeps rising, this creates risk for Will. For example, if the price of SOL continues its uptrend and goes to $175, the party who bought Wills's short calls would be able to execute the option and purchase 1 SOL worth $175 each, for $150 each. In this scenario, Will's loss is $25 (underlying price - strike price) - $5 (the premium which is still kept by Will and helps offset some loss) = $20 loss per option.
Scenario 2 (The price of SOL stays the same):
If the price of SOL stays the same, Will would still have the $5 he sold 1 call of SOL for. He would profit $5 from the premium he received for selling the calls.
Scenario 3 (The price of SOL falls):
If the price of SOL heads lower over time, Will was right! He will profit by keeping the $5 premium he received from selling the call option.

Buying Put Options:
Sol Price: $100
Will thinks that the price of Sol is going down and wants to profit off of this, however, he wants to reduce his potential downside, compared to a short call where the downside is potentially unlimited. Will could buy a put option to accomplish this.
With SOL trading at $100, Will thinks it will decrease by over 10%. A put option contract with a strike price of $90 expiring in a month's time is being priced at $0.30. He decides to go long on 1000 put options with a strike price of $90, costing him $300 (1000 put options * $0.30). Now let’s look at some scenarios:
Scenario 1 (The price of SOL rises):
If the price of SOL rises to $110, Will’s 1000 put options at a strike price of $90 would expire worthless, meaning that Will would lose his initial outlay of $300. This is because the price has expired higher than the strike price of $90.
Scenario 2 (The price of SOL stays the same):
If the price of SOL stays the same, Will’s 1000 put options at a strike price of $90 would expire worthless, meaning that Will would lose his initial outlay of $300. This is because the price has expired above the strike price of $90.
Scenario 3 (The price of SOL falls):
If the price of SOL falls to $89 before expiry, Wills put options are now worth $1.00 since you could exercise them and be short 1,000 SOL at $90 before immediately buying back at $89. Wills's total position is now worth $1000 with a profit on the position of $700 (233%). Using a long put option allowed Will to realize a much greater gain than the 11% fall in the underlying price.

Selling Put Options
Sol Price: $100
Will is bullish on Solana and thinks that the price of SOL is going to rise steadily and that the chance of SOL dropping is incredibly remote. He wants to invest and maximise his gains out of the potential rise, but doesn't have much capital to do so. In order to accomplish this, he might sell a put option.
Will sells 100 SOL put options with a strike price of $90, expiring in three months, for $2.50. These scenarios could occur:
Scenario 1 (The price of SOL rises):
As expected the price has risen, therefore Will receives the premium paid to him. Profit on a short put option is limited to that premium received. Wills maximum gain is therefore limited to $250 (100 * $2.50)
Scenario 2 (The price of SOL stays the same):
Similar to Scenario 1, Will receives the premium and makes a profit of $250. This is because the price has expired at or above the strike price.
Scenario 3 (The price of SOL falls):
Let's say the SOL price drops to $80. Will is assigned to buy SOL at the strike price of $90. In this scenario he makes a loss, however, this would be partially offset by the premium that will be received from selling the option. Therefore the most that Will can stand to lose is $10 (Strike price - current price) - $2.50 (Premium Will received) * 100 (The amount of SOL that Will bought) = $750. The other thing to note is that if Will was bullish on Solana he would just have to buy in at $90 as opposed to the $100 that SOL was trading for when he first started this trade.

You can speculate on price action of an asset through options, the risk is higher, at the profit is higher than just holding. Currently Zeta Market is the most popular dapp for buying futures and options contracts on Solana.
Now, let us look at current Katana strategies based on options.
Katana Strategies
Covered Call:
Covered calls are a popular options strategy in which a trader sells an out-of-the-money call option on an asset while simultaneously holding the asset.
A call option is Out of money if the underlying price is trading below the strike price of the call.
This strategy allows traders to maintain their existing assets while generating instant yield from the contract's premium.
This strategy is generally employed when your outlook on the assets price is neutral to moderately bullish.
The strategy works by first depositing the underlying SOL on Zeta and minting out-of-the-money SOL calls in return.
The vault then sells these call options earning the option premium as the initial yield.
If the price of SOL is below the strike price at the time of expiry, the vault earns the full value of the options it sold and can repeat the strategy, compounding its SOL over time.
Cash-Secured Puts:
Cash-secured puts are another common options strategy in which a trader sells an out-of-the-money put option on an asset.
A put option is out of money when its strike price is lower than its spot price.
In this way, the trader is expressing a relatively bullish market view on the underlying asset and expects it to be above the selected strike price at expiry.
The strategy works by first depositing the underlying USDC on Zeta and minting out-of-the-money ETH puts in return.
The vault then sells these put options, earning the option premium as the initial yield.
If the price of ETH is above the strike price at the time of expiry, the vault earns the full value of the options it sold and can repeat the strategy, compounding its USDC over time.
Depositing and Withdrawing from Katana Vaults(A practical guide)
Now that we know about various strategies Katana Vaults offers. Let us see how we can earn some juicy yields.
Head over to app.katana.so/vaults
Depositing to Katana Vaults:
Step 1:
Select the vault you want to invest in, I will be investing in SOL covered call vault
You can see the description of the vault strategy and the potential risks it involves. We discussed these in the previous sections.
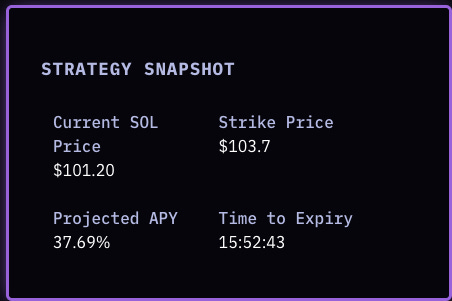
You can also see the strategy snapshot below the risk section.
Step 2:
In the upper right-hand corner, you will see the option to connect the wallet.
The phantom wallet is the most popular wallet on Solana, here is a handy installation guide for it: Create a new wallet.
Once installed, connect it to the website.
Step 3:
Now let us deposit SOL in the vault.
I am depositing 1 SOL in the strategy, you can see your SOL balance in the wallet below. Always enter the deposit amount lower than the total balance to pay for the gas.
Click on submit and approve the transaction on the phantom wallet.
As you can see now the buy balance reduced by 1 SOL and the deposited amount now shows my 1 SOL balance.
Step 4:
Katana vaults operate in a weekly round structure, meaning funds are locked in the strategy during the course of the period. Each period begins on Friday morning EST when the strategy rolls over and new options are minted. At this time, deposits in the deposit queue are initiated into the strategy and begin earning yield.
The funds you deposit now will remain in a deposit queue and will only begin earning yield starting Friday morning EST.
Once your funds are in the strategy you will see the ‘claim shares’ option. These shares represent your ownership of the vault. They can be later redeemed for the underlying plus the accumulated yield over the time period.
Withdrawing from Katana Vaults:
As mentioned before you will start earning only from next Friday. You can either withdraw before that where you will only get the underlying collateral or you can wait till Friday and get the shares and withdraw against those shares to get both the collateral as well as yield.
Step 1:
Head over to the strategy: https://app.katana.so/options/call/sol
Step 2:
Select the withdraw option:
As you can see I do not have any available shares. As discussed before you can use the instant withdrawal function to get the underlying collateral.
Once you get the shares, you will see your available shares above on withdrawing against shares you get both the collateral as well as yield.
Risks, Returns and Fees
Risks
As with any decentralized protocol, it is important to be cognizant of potential risks as a user. Katana is implemented as a set of smart contracts on the Solana blockchain. While the code has been thoroughly tested and peer-reviewed by top engineers in the Solana ecosystem, no codebase is perfect.
Here are some of the risk categories of the Katana protocol:
Smart Contract Risk
Execution Risk
Oracle Risk
All processes have been thoroughly tested and are designed to mitigate all the risk vectors above. That said, we prefer to be fully transparent about potential risks to ensure users are fully informed when using Katana.
Returns
Upon the incorporation of a user's funds into a given strategy, they are minting shares from the vault as a receipt of their deposit. These shares adjust in value over time in order to reflect the cumulative performance of the strategy since the user first deposited.
Current, projected, and historical returns are also available at app.katana.so/analytics.
Fees
Katana has zero fees today across all its vaults. The fee module is built into the code and is currently set to zero. The Katana core team will leave the lever on for governance to select an optimal fee structure to reach protocol self-sustainability via a community vote.
Katana community and Future plans
Katana has a very active community with 23.2k Twitter followers and 12k Discord members.
Katana community members are aptly called Samurais.
Katana attracts a diverse set of community members from traders to coders looking to build their strategies on Katana.
Katana team has also executed community-driven requests including adding mobile support, improving user flows and polishing the UI/UX.
Katana also did an NFT drop to honour loyal, high-value-add members of the Samurai community and provided them with early access to Katana’s vaults.
Katana is open to anyone looking to generate yield on their crypto assets, including but not limited to:
Retail users
DAO Treasuries
DeFi protocols
Institutions
FinTech Applications
In the future Katana also plans to offer automated vault strategies along with structured products currently offered.
Automated Vault Strategies
Passive method to earn yield on a chosen base asset
Span a wider array of yield farming opportunities
Strategies will be changed as new opportunities arise, enabling depositors to consistently earn the best yields available
Fully automated execution for the user
Conclusion
In a world full of crazy APYs and rug pulls. Katana offers a way of generating sustainable yield by packaging complex yield generating strategies into vaults, greatly simplifying the user experience.
Katana comprises of star team that won the first prize in the Solana Ignition hackathon. They recently announced a $5 million seed round led by Framework Ventures. Many other reputed VCs and angels participated in the round.
In the future, Katana will allow user-generated yield earning strategies. These will truly usher the power of web3 and its permissionless nature. Anyone can build upon Katana to package complex strategies into vaults and get exposure to Katana’s sprawling community.
Protocols like Katana also shows the power of composability on Solana. Katana strategies use Zeta markets in the backend to trade the contracts. This is an example of web3 vision of composability coming to fruition. Solana blockchain is one giant computer, devs are building things on top of it and are also leveraging each other’s work to improve user experience, creating an equal playing field for all in the ecosystem.
In the traditional finance world, complex strategies created by asset management companies remained private and out of reach for most users.
Katana looks to revolutionize asset management and become the de facto yield generation layer for DeFi.
Sources
https://medium.com/@katana_hq/introducing-katana-c599bb875231
https://www.kotaksecurities.com/ksweb/Research/Investment-knowledge-Bank/difference-between-futures-and-options#:~:text=A futures contract is executed,feel the conditions are right.
https://www.investopedia.com/options-basics-tutorial-4583012#:~:text=Call and Put Options,-Options are a&text=A call option gives the,payment on a future purchase.
https://zetamarkets.gitbook.io/zeta/introduction-to-derivatives/options-basics/long-call
https://zetamarkets.gitbook.io/zeta/introduction-to-derivatives/options-basics/covered-put
https://zetamarkets.gitbook.io/zeta/introduction-to-derivatives/options-basics/long-put
https://zetamarkets.gitbook.io/zeta/introduction-to-derivatives/options-basics/short-put
https://medium.com/@katana_hq/katanas-mainnet-launch-the-gates-are-open-11e9e3e5798a