A Complete deep-dive into the complex world of Options Trading in the most simplified way and how Zeta is democratizing that on the fastest blockchain — Solana!
The vision of today’s project, which we are going to dive deeper is simple — to revolutionize the Derivatives Market on DeFi. It’s simply a Decentralized Exchange (DEX) built on the Solana blockchain.
Starting with the Options Market, Zeta (ζ) is enabling anyone to effectively hedge risk against crypto market movement & events. It’s the premier under-collateralized DeFi derivatives platform, providing liquid derivatives trading to individuals and institutions, without any discrimination. The best part is, it’s powered by Serum, the premier exchange protocol on Solana!
Zeta Markets was started as a project by two university friends, by participating in the Solana Season Hackathon, and then, they ended up not only winning it but scaling the product further with a rapid pace of development and then raising a whopping $8.5 Million from the world’s leading investors🤯.
To get started, we will understand more about Zeta Markets, but first, let’s understand the basics of a kind of derivative i.e Options, and then how Zeta is bringing Traditional finance’s derivatives trading capabilities to DeFi and what lies ahead for Zeta.
LFG🚀
The Complex World of Derivatives🌎
Derivatives present an important tool for traders to make bets on price, volatility, interest rates, tax, and many more factors. In fact, most of the traditional finance volume belongs to Derivatives! While there are many derivatives, that you might have come across, the most popular are Futures & Options, which derive their value from an underlying asset like stocks, commodities, or even cryptos.
To understand derivatives, let’s start with an example: Let’s say, you want to make a $100 bet with your friend by signing a contract, that Solana will cross $200 in 3 months — this is simply a derivative (Today’s Solana price being $100). You are not actually owning the Solana, but you are exposing yourselves to a bet, which derives its value from Solana. This was the simplest derivative, but they are a lot complex and can come in any form.
The next you might be wondering is, what the hell is “Options”
Understanding Options 📈
As the name depicts, Options are literally the “Option” to buy or sell an asset at a future date! For example, buying Solana (SOL) Options at a strike price of $100 would mean, you will have the right to buy Solana at $100 after 3 months, whatever be the price of Solana. So, if the price of the SOL is $200 after 3 months, a trader will simply buy the SOL at $100 from the options derivatives, and then sell it at $200. Simply, a profit of $100. Now, if the price of SOL is $50 in the market, the trader wouldn’t like to buy the SOL at $50. He will simply reject the option to buy. This is simply the ‘call option’.
You may be wondering, the option buyer has a win-win situation because he can only exercise options when it benefits him?🧐
Obviously, there’s no free lunch in finance. So, every option has a price that the buyer pays to the seller. This is called the premium and is paid regardless of whether the buyer exercises the option or not (You can think of it as the price you have to pay to get into this type of Contract). Let’s suppose, in our example, the premium is $10 .
Continuing on the above example, let’s consider three scenarios:
If the price of SOL is less than $100 on the expiry date, it would not be profitable for us to exercise our option at $100. This option is called an out-of-the-money option (OTM). The loss will be equal to the premium of $10, which the “Option seller” would receive.
If the price of SOL is $100 on the expiry date, that option becomes the At-The-Money option (ATM).
If the price of the option is more than $100, then the option becomes In-The-Money. But, we will make a profit only if the price is above $110 since we have already paid a premium of $10.
In the real world, the parties do not sell anything to each other, but only pay the difference in the price of the asset and the strike price.
Now you might still be wondering what are those and ‘Call’ and ‘Put’ terms associated with Options
Let’s try to understand in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
Call option
A call option has 2 entities involved in it.
Call buyer
Call seller
Now let’s go one by one. Taking the earlier example
Call Buyer: Raj is bullish about SOL and his assumption is that SOL is going to go even past that, then there he has a potential upside in SOL going up but he wants to minimize his downside if SOL goes down.
What he will do now?
he will buy a Call option!
(To understand the specifics more deeply, head over to the Zeta market docs)
💡Tl;dr
What’s the view? Why trade in it? You are Bullish on an asset in a certain time frame.
What’s the cost? The Premium you pay
Max Profit: Unlimited upside
Max Loss: The Call option price you paid to enter this position. So limited downside
Breakeven at expiration: The strike plus the price you paid for the call.
2. Call seller
Let’s go one by one quickly!
What’s the view? You are sort of Bearish or think the asset will go Sideways, or you want to hedge against your previous position for risk adjustment,
What’s the cost? No cost! you get paid the premium to sell calls
Max Profit: The premium you get paid. (Oh! yes, you put a cap on your potential profits here)
Max Loss: Unlimited, if the price of the underlying asset rises.
Breakeven at expiration: The strike plus the price you paid for the call.
2. Put Option
Here we also have the 2 entities
Put buyer
Put seller
You might be drawing analogies across this two and you are right! that, it’s kind of similar but works differently.
Put Buyer:
Call seller and Put buyers are somehow similar. Put buyer is 100% bearish (it must go down) but the Call seller has a side-wise view(either sideways or bearish).
one common point is that both are Bearish about the asset.
What’s the view? You are bearish on the asset.
Cost: The premium you pay.
Max Profit: If the asset goes to zero, you make the difference between the strike and zero, minus the premium you paid.
Max Loss: The premium you paid for the put.
Breakeven at expiration: The strike minus the price you paid for the put.
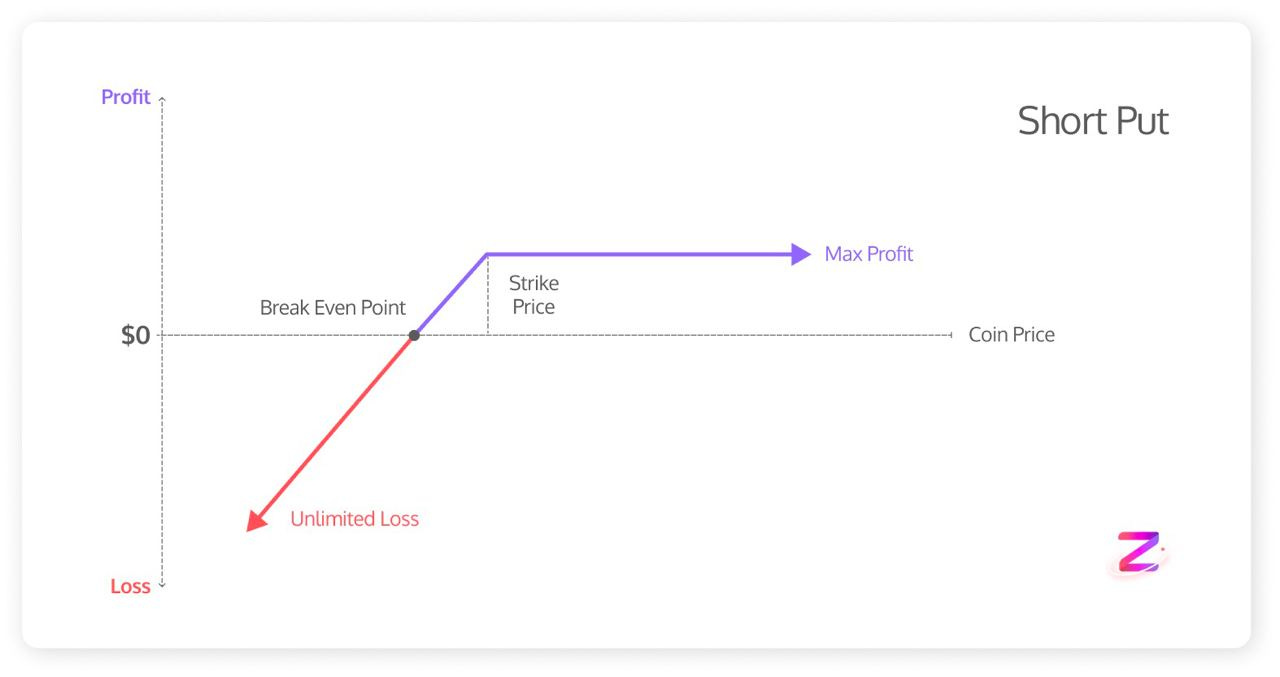
2. Put Seller
Call Buyer and Put sellers are somehow similar. Call buyer is 100% Bullish (it must go up) but the Put seller has a side-wise view(either sideways or bullish). one common point is that both are Bullish about the asset.
What’s the view? You think the underlying asset is staying stable or rising steadily. You don’t have much capital to buy the underlying or are waiting for a dip to buy the asset.
Cost: None
Max Profit: The premium paid (limited)
Max Loss: The strike price — premium paid * amount (unlimited)
Breakeven at expiration: The strike price — premium
In a nutshell!
What are Covered Calls?🧐
Selling a call option when the underlying asset is held by the seller is called a covered call
In simple words, you are covering any potential losses or gains, by taking an opposite bet. You can do the same with the “Put options” as well. Everything is just the opposite, in the case of the “Covered Put”. The difference, being Only they are bought based on a decrease in the price of the underlying asset. These are the Options Strategies.
Now it’s time for us to take look at a new landscape, DeFi! and How Zeta is democratizing Derivatives in DeFI.
Derivatives on DeFi📈
While DeFi is booming with leaps and bounds, the Centralised Exchanges still make up the lion-share of options trading, with Centralised Bitcoin Options Open Interest peaking $15 Billion, last October! The reason is, these centralized exchanges offer institutions and large traders a framework that is regulatorily compliant and capital efficient.
While these serve the needs of big clients well, there is a need for decentralized alternatives that are open and permissionless — to cater to the masses!
What are the current limitations of DeFi Options?🙁
Options are a mammoth in traditional finance and are growing tremendously on centralized exchanges, but it’s yet to catch on core DeFi rails. Here are some of the reasons, why:
High cost of options: On-chain Transactions are costly!
Low capital efficiency: In DeFi, most of the instruments are over-collateralized, decreasing the overall efficiency of the product due to a lack of leverage.
Imperfect pricing: Due to lack of liquidity (low trades volume), pricing is not perfect.
Lack of complex margining: Traders need more flexibility in terms of margins.
Lack of liquidation mechanism: Due to limitations of the DeFi platform
Zeta solves these with its core innovations and efficient mechanisms. Here is how👇👇
Enter Zeta — The Options Messiah on DeFi!
Zeta Markets is a best-in-class under-collateralized DeFi derivatives platform that specializes in Derivatives.
Zeta’s goal is to provide a platform where traders aren’t sacrificing ease of access, capital efficiency, or liquidity, and instead have a professional-grade platform to trade derivatives on a number of crypto-centric underlying.
Zeta enables the trading of options on a liquid, non-custodial market — with all the latency benefits of a centralized exchange. Zeta is THE first DeFi option protocol that pairs (1) fast, under-collateralized options trading with (2) deep liquidity, driven by a hybrid order book and unique options AMM.
But What they are? let’s understand what Zeta offers one by one
Key features of Zeta markets⚡
1. Liquid Option Markets 🌊
In DeFi the option liquidity usually remains poor either because of inefficient pricing offered by poor AMMs or the unreal transaction fees. Liquidity is an essential component for the efficient operation and accuracy of an asset in any market. It ensures the depth of matching buyers with sellers.
Though in Traditional finance order book is a tried and trusted method for price discovery, when it comes to DeFi its success has been relatively poor. It is poor due to the complexities in building a performant on-chain matching engine, as well as the prohibitive transaction fees associated with them. So Zeta leverages Serum’s order book infrastructure to provide the most efficient price discovery and trading infrastructure for all our options markets.
Zeta uses a hybrid approach, leveraging the order book for deep liquidity and the OMM(Options Market Maker) to underpin market participation. It integrates the two into the platform where users can trade against one another, and also can also fall back to orders placed by the OMM when an active counterparty to trade with isn’t available.
This allows all market participants to provide liquidity, and in doing so derive the best price for all participants.
2. Under-collateralization 📦
The existing DeFI options platforms require traders to fully or over-collateralize their positions to overcome future liquidation/over-bankruptcy issues. Which makes it an inefficient capital system which is restricting in nature.
But Here Zeta enables Under-collateralization. Does that mean it has become riskier? let’s find out! Zeta utilizes the following core mechanisms to enable under-collateralized options trading:
Portfolio Margining System Locks up collateral while being aware of existing risk profiles.
Liquidation Engine Oversees trading positions and ensures that sufficient levels of collateral are maintained to service their open positions (taking into account their current PnL).
On the other hand, when selling options, one can end up being exposed to theoretically unlimited risk. As a result, Zeta protects itself and users from potentially large losses by requiring them to front some initial collateral, calculated by a formula (We won’t discuss that here as it’s beyond the point of the essay, check out Zeta’s whitepaper to know more).
Liquidation
Zeta uses a liquidation engine to secure the trading network against at-risk positions in order to minimize the impact on market participants. The liquidation engine is used to identify positions that move below their maintenance margin.
Insurance Fund
An Insurance Fund is there to cover events of mass liquidations. Which is funded from the platform’s trading fees.
3. Speed and Efficiency
Building a derivatives protocol on Solana provides traders the ability to trade at lightning speed on the Serum order book with almost zero cost, unlike current platforms which force developers to build parts of their program off-chain or on Layer 2 to keep costs down for their users.
4. Zeta’s Robust Options Pricer
Zeta uses the Black-Scholes-Merton (BSM) formula — Black-76. for options pricing, a tried and tested mathematical model in TradFi.
The model inputs:
Forward Price: Is calculated using the underlying price provided by the oracle, the risk-free rate, and the time till expiry.
Volatility: Of the underlying asset is calculated by the on-chain volatility surface that the OMM maintains.
Risk-Free Rate: Is derived by the OMM which stores the risk-free rate curve.
Strike: Is the price predefined in the contract for which to buy or sell the underlying — this a parameter defined in the options contract.
Time to expiry: Is the point in time when an option will be exercised — this is a parameter defined in the options contract.
Using these parameters and the Black-76 pricing equation, the options price is determined by the OMM
In order to quote market-driven prices and minimize any risk imbalances, Zeta uses a global volatility surface as its key input in pricing every option, which will adjust for the supply and demand of volatility. To implement effectively it utilizes a dynamic volatility calculation that will be updated based on real-time trade data within zeta markets.
5. Decentralized Option markets and OMMs
Many established options markets in DeFi use an AMM to price their premiums. Though AMMs are great for bootstrapping the liquidity of a market, however, they leave important variables(like dynamic volatility) out of scope when it comes to pricing options. This can lead to stale prices on the premium of the options, and as a result, can generate large amounts of impermanent loss for liquidity providers.
Order books allow you to state the exact price for the purchase or sales of your options. The order book is a tried and trusted method for price discovery and has been successfully used across traditional finance. With order books, fulfillment of your order is not guaranteed, and you must wait for someone to take the other side of your trade. Here Zeta leverages Serum’s order book infrastructure to provide the most efficient price discovery. Project Serum is an on-chain order book-based decentralized exchange (DEX).
The Zeta in effect, combines the options AMM model, with an order book to provide a hybrid options market consisting of both the order book and an options market maker (OMM). The OMM is a virtual counterparty that helps bootstrap the market, sending orders directly to the Serum order book, and providing a baseline level of liquidity for traders to buy and sell options against. The OMM gives liquidity providers a way to interact with Zeta passively through its robust options pricing algorithm. The OMM can be thought of as a communal market maker which can provide liquidity in situations where the order book tends to be thin. Its liquidity is provided by a liquidity pool, into which any users can deposit funds and earn a passive yield from the strategy as well as trading fees on Zeta.
Those are the most prominent Features that Zeta offers. But still, there are some exciting concepts left, which will help you understand Options in DeFi and Zeta’s dynamics better. 👇👇
How the Margin is calculated in the Zeta protocol
Now let’s take a look at Best in class Robust Margining system of Zeta which makes derivatives trading on DeFi bulletproof.
Margin system
For an asset class as volatile as crypto, we know that minutes can be precious. This has made it impossible to create an effective margin system. In DeFi we have typically seen over-collateralization. The other blockchains have typically been slow, so often it takes minutes for a protocol to know the real state of the underlying asset price and take the actions required to keep the protocol safe and sufficiently collateralized.
Zeta with the Help of Solana’s 400ms block time which is incredibly fast, solves this. This enables zeta to update prices and monitor positions multiple times per second. Which indeed implements the margin system that allows for an under-collateralized trading experience.
there are three factors that contribute to doing this
Mark pricing: Zeta with its own pricing mechanism calculates the Mark price of all tradable assets and uses this to inform the margin and collateralization system. Without this, it is impossible to know and determine the PnL and their risks, which is important for the under-collateralized options that zeta provides.
Collateral Framework: The collateral framework is what ensures that this balance is maintained so that the exchange at large can continue functioning.
Liquidation Mechanism: This liquidation mechanism allows liquidators to step in when a user’s trading account is too risky to continue trading. When this occurs the user is liquidated to ensure that the losses do not extend beyond isolated users and cause Over-bankruptcy.
Socialized loss & Impermanent loss
This Socialized loss comes from the Liquidation mechanism we were discussing earlier, If both the liquidation process and the insurance fund fail to cover over-bankruptcy, losses will be shared across depositors in the Zeta platform.
But If this happens then there is another risk of the existing capital getting withdrawn. So to prevent that there will be an over-bankruptcy ratio implemented to withdrawals ensuring that the platform has sufficient capital to continue operating.
Impermanent loss in an Options OMM
Impermanent loss is a well-heard concept around AMMs. It is a loss that funds are exposed to when they are in a liquidity pool.
This loss typically occurs when the ratio of the tokens in the liquidity pool becomes uneven and is typically calculated by comparing the value of your tokens in the liquidity pool versus the value of simply holding them.
Participants in the options OMM are taking on a variety of risks which can be cataloged via the options greeks. These risks are exposures that can cause the OMM pool to win, as well as experience losses.
To know more and go deeper into these interesting concepts head over to their docs to know more.
Zeta Infrastructure under the hood
Developer resources: Zeta SDKs
Developers can use Zeta’s open-sourced SDK on devnet. Which is a typescript library and you can interact with the Zeta program smart contract using that SDK.
On ground Trade Process
1. Account Opening
Place your stablecoin collateral into one of two accounts: a. User Vault — holds the collateral for an individual user trading options b. OMM Vault — holds the communal liquidity pool supplying Zeta’s OMM
2. Trading Market participants can send options orders to the orderbook, and trading is just as it is on any CeFi exchange with sub-second latency, multiple order types, and real-time risk management.
Alternatively, the OMM can take care of all of this, and it will send out market-making orders on behalf of the OMM pool.
3. Liquidation Zeta marks positions in real-time, recognizing unrealized PnL as the market moves. In the event that a participant falls under their maintenance margin, their at-risk position is liquidated at the current market price. This losing position can then be taken over by any other participants (including the OMM, which acts as a backstop).
4. Settlement At the time of expiry, Zeta collects all outstanding instances of a given option, as well as querying the price of the underlying asset from an oracle. It calculates the net profit and loss to each trader and credits or debits their account as appropriate.
5. Withdrawal Users can withdraw their funds however they wish at any time.
Zeta’s user-friendly UI
Take a look at this sleek-looking UI. And explore what it does…
Trading guide
Step 0: Visit mainnet.zeta.markets, there you will be a t&c pop-up, after agreeing, Connect your wallet.
Step 1: After connecting you’ll get to choose what to trade. Here let’s go with Options and show you how to trade in Zeta.
Step 3: To buy options toggle the tab to option on the mid-left dashboard. Select between Call or Put.
There will be a number of available options contracts shown to you. Choose the one you like according to the price and expiry date you’d prefer.
Step 4: On the top right dashboard you’ll see the Buying options with the description(thanks to zeta’s great UX it’s very intuitive and simple).
Then you buy that with that quoted price and quantity you choose.
Step 5: After buying you will be prompted will that transaction to approve on your wallet, after approving you can see your positions in the Account equity tab.
And Voila! you have bought an options contract🎉!!
now wait till the expiry date and see whether you are exercising the contract or not.
Advantages: How is Zeta better than others?🤔
Options Market Maker:
Zeta’s best-in-class OMMs on Solana give derivatives a fast CeFi experience on DeFi options.
Zeta FuZe & Composability:
Zeta FuZe is a “cross-program invocation library” (https://github.com/zetamarkets/fuze) that allows anyone to make cross-program calls and programmatically interface with Zeta’s smart contracts. By focusing on tooling and integrations Zeta positions themselves to be easily composed with. Furthermore, outside parties can automate trading using bots creating a positive impact for the ecosystem as a whole.
As we have seen in many instances — the creation of strong tooling can set off a virtuous cycle for an app ecosystem that leads to more organic engagement, TVL, etc.
UI/UX & Mobile-first approach:
Most of the DeFi apps look very technical. And as the ecosystem is so engineering-heavy that start-ups must often prioritize the underlying tech at the expense of good UI/UX. Good UI/UX is a moat!
Zeta took great lengths to also design a mobile-friendly experience after discovering that a majority of their users wanted to be able to access Zeta remotely.
Community and Backers
“ZetArmy”! Yes, that’s the nickname of the vibrant Zeta Community. The community has stepped up big-time from helping the team, designing its loading-screen visuals, multi-language translations, or just alpha-testing the product, many people have been involved in Zeta, right from the start.
With Decentralized community governance of its roadmap, Zeta wants to align its wide range of stakeholders that interact with the protocol, including traders, market makers, developers, and other service providers, and mature into a DAO, where the community can vote on the future direction of the protocol.
Partners and LPs
Zeta has seen blazingly fast traction with protocol partners in Serum and Pyth, institutional uptake from crypto derivatives firms, and DeFi native sources of demand in structured product and risk management protocols. Zeta is backed by the most prominent and active Investors of the ecosystem like JumpCapital, Electric Capital, Alameda research, Solana, and more…
Partnering with fellow Projects Zeta has been creating a convenient and more useful ecosystem for its users while making it a win-win situation 🤝for the associated projects growing altogether.🚀
Wrapping Up the NASDAQ for DeFi Options
Zeta markets is on the verge of making the DeFi ecosystem more powerful. 🚀
Zeta is built upon a solid fundamental reality, Derivatives!. Which has proven itself from times to remember. And now it’s the turn for Zeta to unleash its power, to make this reality more prominent in a Decentralized way.
Will than happen? That’s the option they have both literally and metaphorically. And It will be exciting to see how things get exercised!
We are ready with our Zeta flavored popcorn 🍿. Are you?
This was a complete deep-dive into the Zeta markets, making DeFi derivatives better. If we missed something or you have any suggestions or just want to have some interesting conversations around web3, we would love to connect — Yash Agarwal and Sitesh
Until then…
References
Some of the Images and numbers are taken from Zeta’s official sources and the third parties referenced. If you want to know more you can also read their docs. The information contained herein is for informational and entertainment purposes only. readers are advised to do their own research before making any decisions. Read the full Disclaimer.