Empowering DeFi 2.0: A Timeswap Deep Dive
A deep dive into Timeswap’s protocol (Need for it, How does it work, How to get started, Utility of Time Tokens, and many more!)
The cryptocurrency’s vision is simple — to make money and payments universally accessible. DeFi (Decentralized Finance) takes it a step further by integrating other financial services — savings, loans, trading, insurance, and more! The most innovative solution that emerged in the first wave i.e DeFi 1.0 was AMM (Automated Market Making). It made DeFi 1.0 truly decentralized by replacing the Traditional Order-Book system (centrally matching all orders) to algorithmically creating liquidity pools (LP) of tokens and enabling their trade (no central or human intervention). Sounds Complex?
Let’s first understand AMM in detail and then move towards our spotlight protocol i.e Timeswap. Even if you are totally new to DeFi, just stick to it — it’s completely beginner-friendly. Let’s go🚀
AMM — DeFi 1.0
Before AMMs, Traditional exchange platforms enabled people to offer different prices for buying and selling assets. After some time, other users select a listed price that they agree with. That price goes on to become the market price of the asset. It’s called Order Book Model. Yes, our centralized exchanges (CEX) like Coinbase, Binance, and traditional exchanges like NASDAQ works in this way. The problem was — the traditional market-making process requires professional market makers (Liquidity providers) who handle a lot of orders. So, they are expected to quote the volume they can trade along. They are limited in terms of the frequency with which they can quote the best prices.
AMMs offer a newer alternative to providing Liquidity. What started as a proposal by Vitalik Buterin, was pioneered by Uniswap, followed by other protocols like Curve, Balancer, etc
But, What’s AMMs? It provides traders with a new option by creating liquidity pools. They also incentivize liquidity providers to place more assets into the liquidity pool. The more assets there are in a pool, the larger trades it can support. Users no longer need to just trade between buyers/sellers. What users do is trade against the liquidity pool.
The “pool” in “liquidity pool” is quite literal. When users contribute to a liquidity pool, they increase its liquidity, enabling traders to make larger swaps at the market price. Why Do People Contribute? Liquidity providers earn fees when traders interact with a pool.
A mathematical formula is used to price the tokens inside it. In AMMs, the formula may be tweaked in various ways to optimize the pool for different purposes, to better facilitate swaps between different types of tokens. For example, Uniswap uses a constant product protocol (x*y=k). Let’s understand it quickly by an example. Assume you are a trader, buying ETH for DAI.
The key formula to keep in mind is x * y = k, where x and y are the coin quantities in the liquidity pool, and k is the product. In order to keep k, constant x and y can only move inverse each other. When you buy ETH, you are increasing x (as you are adding DAI to the liquidity pool) and decreasing y (as you are removing ETH from the liquidity pool). The price of x decreases, while the price of y increases making the constant equal to the k again. y/x represents the price of the trading pair.
This completely changed DeFi and made trading between Crypto/Token pairs very efficient and even allowed trading exotic pairs (less popular token pairs).
A defining moment in the evolution of DeFi was the launch of Uniswap in 2018 which was the first Automated Market Maker(AMM) built on the concept of liquidity pools. Uniswap’s AMM enabled permissionless exchange between any ERC-20 tokens which opened up liquidity for long tail assets.
Our spotlight protocol, Timeswap wants to do a Uniswap moment, but for borrowing, lending, and collateral instead of buying & selling crypto pairs.
What’s Timeswap?
Let’s try to understand first in layman terms and then, dig deeper into details. Timeswap is a lending and borrowing protocol for tokens built on the Ethereum blockchain. The lending and borrowing protocol is defined for tokens, specifically ERC20 tokens (Technical standard for Tokens which are built on Ethereum blockchain). That means anybody with an ERC20 token can lend theirs or use it to borrow other ERC20 tokens. There are already a lot of borrowing and lending protocols in the market, so, what makes Timeswap unique?
Timeswap is the first fully permissionless, oracle-less, non-liquidatable, capital-efficient, fixed maturity lending and borrowing protocol, using a unique 3 variable constant product AMM.
This is their official definition. Let’s decode each bolds one by one to understand what makes Timeswap unique — its features:
Fully Permissionless
A permissionless design implies that the given product or protocol is openly accessible to the public and doesn't require any permission. For instance, Uniswap is permissionless via a constant product AMM model. Timeswap takes a step further and makes a permissionless listing of collaterals. Timeswap allows anyone to create a pool for lending and borrowing of any ERC20 tokens with any other ERC20 token as collateral with any maturity date.
Oracle-Less
What are Oracles? They are entities that connect blockchains to external systems, thereby enabling smart contracts to execute based upon inputs and outputs from the real world. For instance, a lending and borrowing protocol would have depended on Oracle to get market interest rates and token values. It though comes with a drawback — they are exposed to threats and scams. Timeswap is unique, it doesn’t even have oracles, hence, no risks of threats.
But, how does it get market data?
Just like Uniswap, it has its own internal ecosystem — Supply and Demand to determine the parameters. Lender, borrowers, and liquidity providers interact with the Timeswap pool by executing lending and borrowing transactions, thus influencing the supply of assets which in turn influences the interest rates and minimum collateral required for each transaction.
(We will explore more on the price discovery later once we understand the Timeswap AMM model)
Non-liquidatable
When the borrower’s collateral asset starts dropping in value, the protocol starts selling the asset (liquidating) up to a point, where they can no longer support the loans. Timeswap doesn't liquidate these assets, instead, their collaterals are distributed among the lenders of the Timeswap pool. This eliminates any need for dependency on liquidators or liquidation penalties.
Capital Efficient
In current protocols, deciding Assets as collateral for loans is a cumbersome task, and a lot of assets remain unexplored. Timeswap solves this by designing a system with market-based interest rates and collateral factors. Just like Uniswap, it can potentially allow millions of possible asset combinations.
Fixed maturity lending and borrowing protocol
Let’s divide this into — Fixed Maturity and Lending and Borrowing protocol. In traditional finance, Fixed maturity instruments are very common — like Bonds or Term Deposits. Here, investors deposit their funds for a specified period of time. During this time, they usually cannot withdraw any percentage of the invested amount.
Now, Let’s add Lending and Borrowing into it. Here, participants lock a transaction (either lend or borrow) at a predetermined rate for a fixed time period and not be worried about the changing market rates. Timeswap provides a fixed maturity pool of token pairs from which participants can lend tokens or borrow from. This is a game-changer for the growing crypto money market, where many investors can park their tokens and earn some yield.
Phew!😪 Lots of features, but we have the most important one left, which makes all of the above possible in practice.
3 variable constant product AMM
Remember, we discussed Uniswap’s constant product AMM. Inspired by the Uniswap protocol (X * Y = K), Timeswap employs a 3 variable constant product:
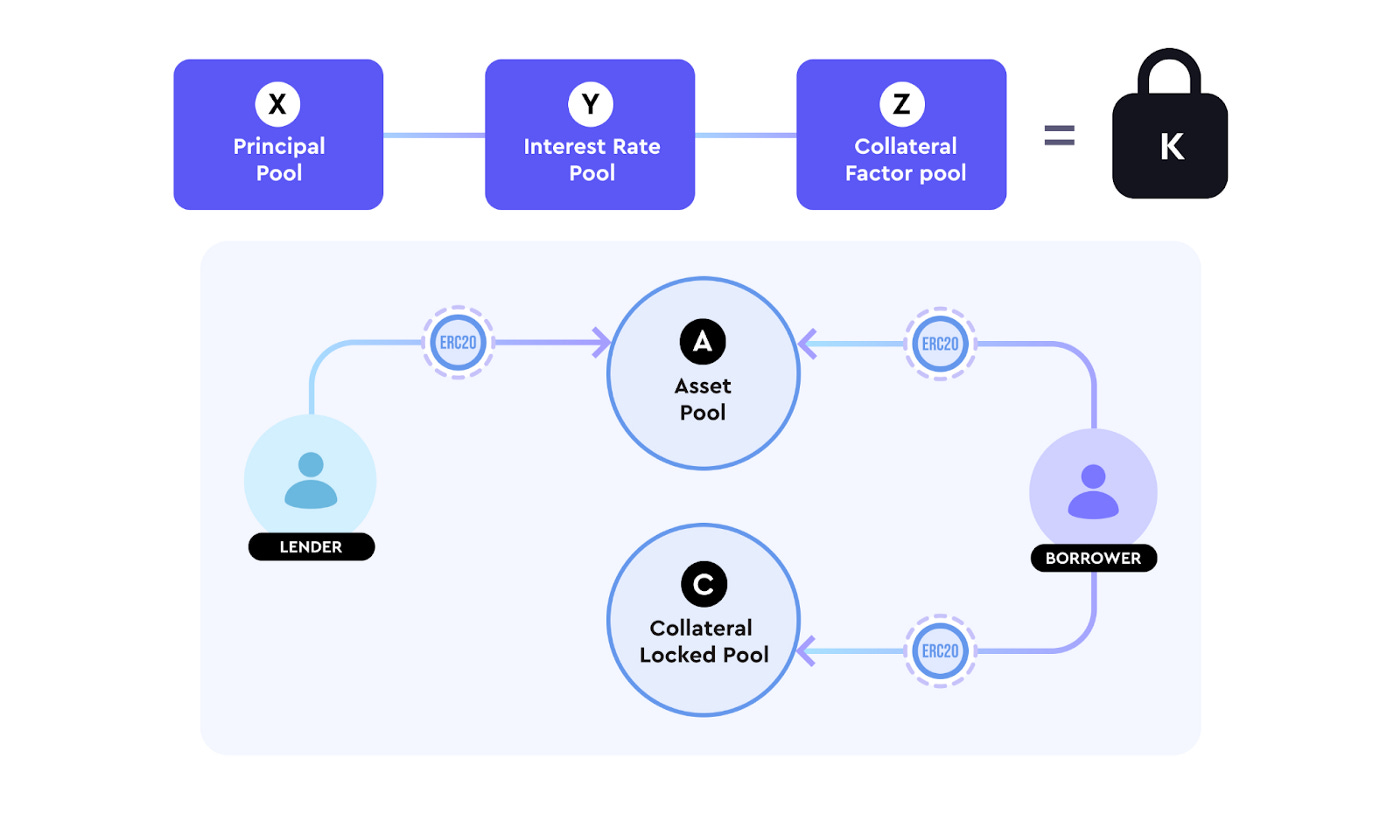
X * Y * Z = K
where,
X = Principal Pool is equal to the number of assets in the pool that can be borrowed.
Y = Interest Rate Pool determines the interest amount per second of the pool, such that ratio Y/X is the max interest rate per second of the pool.
Z = Collateral Factor Pool determines the collateral to be locked by the borrowers such that ratio Z/X is the minimum Collateralized Debt Position(CDP) of the pool.
K = Invariance Constant product
This equation derives the most critical part — Price discovery!
Price Discovery
By the constant product equation, we get real-time market price discovery of interest rate & collateral factors as the principal changes. Let’s understand👇
Lenders add assets to the Principal pool which increases X. To maintain the constant product, Y and Z will decrease which in turn reduces interest rates & CDP/insurance coverage for the next lender.
Borrowers withdraw assets from the Principal Pool, reducing X . To maintain the constant product Y & Z will increase thereby pushing up the interest rate and CDP.
Apart from price discovery, it also solves one more important thing — Risk Profiling.
In current products in the market, the risk profile for investors on specific assets is the same for all and they don’t offer Investors the flexibility to change their risk/return profile based on their needs. Timeswap gives users the freedom to decide the asset pair to cater to as well as the time of maturity. They can adjust their expected rates on the amount being lent or borrowed for a period of time and thus control their risk profile.
Enough of understanding Timeswap’s features, now let’s understand how you can get started with Lending & Borrowing in Timeswap!
Lending and Borrowing: How does it work on Timeswap
To get started with Timeswap, first, you need to connect the Metamask wallet (it may soon add more wallet integrations) and once, you have connected the wallet, you can use all your existing tokens and coins to lend and borrow.
Just like Uniswap has liquidity pools, Timeswap also has a Timeswap pool which has a collection of funds.
A Timeswap pool has 4 parameters:
1. Asset: An ERC20 token being lent or borrowed
2. Collateral: Another ERC20 token
3. Time: Time to Maturity
4. Interest Rate: The rate at which it is lent or borrowed.
There can be three types of users of Timeswap:
a) Liquidity Providers:
Just like other protocols, an LP’s job is to make the Timeswap pool more liquid. For example, an LP can construct a pool of DAI-MATIC (both ERC20) tokens with a one-year maturity date. He must deposit DAI tokens in order to maintain capital liquidity, and he is in charge of facilitating lending and borrowing transactions. He is compensated with a transaction fee as a result of this.
b) Lender:
The user in the above image has 450 DAI tokens that he can lend, and he picks MATIC tokens as collateral, as well as a favorable APR (Annual Percentage Return). He can tailor his APR within a given range based on the number of tokens he is lending. On the screen, the quantity of DAI tokens he will receive upon maturity is displayed, as well as the amount of MATIC tokens that will be sent to him if he defaults.
c) Borrower:
The user in the image above wishes to borrow 450 DAI tokens. He can now adjust his risk once more. The amount of DAI that the user must repay upon maturity, as well as the amount of MATIC that must be locked as collateral, are displayed to the user.
If the borrower defaults, the lender can seize the collateral.
Time Token: Timeswap Native Tokens
Timeswap has a suite of native tokens, that act as receipts for every action conducted on Timeswap. There are four tokens native to Timeswap pools: Bond, Insurance, and Liquidity tokens which are ERC-20 tokens, and the Collateralized Debt Token, which is an ERC-721 token, an NFT.
Now, all of this has its own significance:
For a Lender, if you want to exit your position before maturity, you can freely sell your Bond or Insurance token in secondary markets and exit your position since both of these tokens are ERC-20s. Alternately lenders can choose to partially exit either Bond or Insurance tokens to better manage their yield.
As a borrower, the Collateralized Debt Token being an NFT allows them to down-sell their loan to a secondary party on Opensea. This allows one to create a secondary market for the loans as well.
As the Liquidity Tokens are also ERC-20s, Liquidity Providers (LPs) can down-sell their position in the secondary market and exit their position before the maturity of the pool, thereby allowing deeper liquidity for the pools and free movement of capital in and out of the pools.
Timeswap’s Community
Timeswap has a very vibrant community — which keeps interacting, making memes, participating in testnets, and is very bullish on Timeswap’s vision. They also have dedicated ambassadors progamme called ‘Time Guardians’ which will interact closely with the team, help build a DeFi community from scratch, volunteer with community-building events, and make Timeswap’s community the coolest in DeFi.
Conclusion: Timeswap to the Moon🚀
Given a lot of interesting features, and a strong community of 28K+ members, Timeswap is all set to roar and do a Uniswap moment for Lending and Borrowing. With Money Markets growing in importance, the market opportunity to cater is huge.
P.S: I genuinely love their motto in the whitepaper — “automated in the center, humans at the edges”.
That’s all folks! Feel free to DM me on Twitter (@yashhsm), for discussing anything Web3!
Note: Some references have been taken from Timeswap’s medium page: timeswap.medium.com, Timeswap’s whitepaper, and Timeswap’s Youtube channel. Do check them out!
Additional References:
1. Scalar Capital’s AMM (Kudos to them for a great explainer on AMM)
2. Himadri’s Deep Dive (A good reference explanation on how Lending and Borrowing works, do check this out)